Have you ever wondered how modern engines strike a balance between performance, efficiency, and emissions control? Enter the exhaust gas recirculation system – a vital component in both diesel and petrol engines that plays a crucial role in achieving these objectives.
But what exactly is an EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) system and how does it function within the complex workings of internal combustion engines? In this article, we look into the details of EGR technology exploring its principles, mechanisms and the critical role it plays in the pursuit of cleaner, more efficient automotive propulsion.
What is an Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)?
The exhaust gas recirculation system is a technology employed in internal combustion engines to reduce harmful emissions. The exhaust gas recirculation function happens by diverting a portion of exhaust gasses back into the engine’s combustion chamber where they mix with the incoming air-fuel mixture.
This process helps lower the combustion temperature and decrease the production of nitrogen oxides (NOx), a major contributor to air pollution. The significance of reducing emissions in engines lies in mitigating environmental pollution and adhering to stringent emission standards while ensuring optimal engine performance.
Major Components of the EGR System:
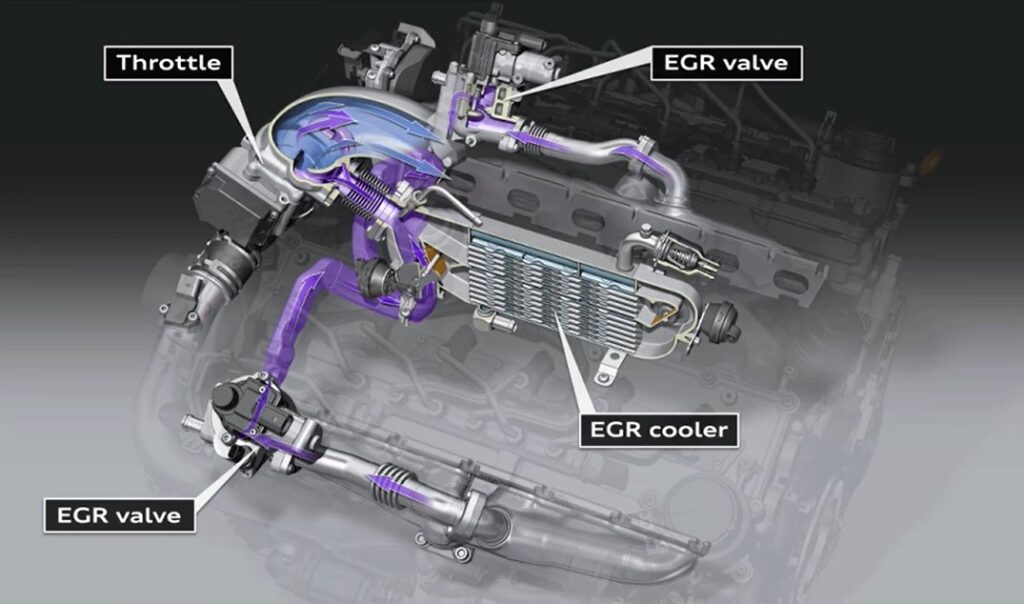
The following are the components of an EGR system:
EGR Valve:
The EGR valve controls the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. It opens and closes based on signals from the engine control unit (ECU) to regulate the amount of recirculated gases, ensuring the desired EGR flow rate.
EGR Cooler:
The EGR cooler cools down the recirculated exhaust gases before they are reintroduced into the engine. By reducing the temperature, it prevents excessive heat from affecting the combustion process and helps improve engine efficiency.
EGR Control System:
The EGR control system consists of various sensors, actuators, and the ECU. It manages the EGR flow by monitoring engine conditions, such as temperature, load, and speed. Based on this information, it adjusts the EGR valve’s position and controls the recirculation rate for optimal engine performance and emission reduction.
Must Read: What is The Difference Between Petrol And Diesel Engines?
How EGR System Works in Diesel Engines:

EGR systems in diesel engines play a crucial role in reducing emissions of carbon dioxide and other harmful gases. They operate by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake system. This process has several advantages and unique challenges. These challenges need to be addressed for effective implementation.
Working Principle of EGR in Diesel Engines:
In diesel engines, the EGR system redirects a portion of the exhaust gases into the intake manifold. This dilutes the oxygen concentration in the combustion chamber, resulting in lower peak combustion temperatures and reduced formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx) during the combustion process.
Benefits of EGR in Reducing NOx Emissions:
The primary advantage of EGR in diesel engines is its ability to significantly reduce NOx emissions. By introducing inert exhaust gases into the combustion chamber, the formation of NOx is suppressed. This helps engines comply with stringent emission regulations while improving air quality and reducing environmental impact.
Challenges and Solutions in Diesel EGR Implementation:
Implementing EGR in diesel engines presents certain challenges. One issue is the potential for increased particulate matter (PM) formation due to the recirculated exhaust gases. To address this, modern EGR systems are often equipped with advanced filters to minimize PM emissions. Additionally, managing the EGR flow and maintaining optimal engine performance can be achieved through sophisticated control strategies and advanced sensor technologies.
Must Read: Too Much Oil in Car Engine Symptoms & What to Do
How EGR Works in Diesel Engines:
EGR Flow Rate and Control Strategies:
The EGR flow rate in diesel engines is carefully controlled to achieve the desired balance between emission reduction and engine performance. Control strategies involve monitoring engine parameters such as load, speed, and temperature to determine the appropriate amount of exhaust gas recirculation. This is achieved through the EGR valve, which adjusts the flow rate based on signals from the engine control unit (ECU).
EGR System Integration with Engine Management:
EGR systems in diesel engines are integrated with the engine management system to ensure optimal operation. The ECU communicates with various sensors to gather real-time data on engine conditions. This information is used to calculate the ideal EGR flow rate and adjust the valve accordingly. The integration allows for precise control, maximizing emission reduction without compromising engine efficiency.
EGR Troubleshooting and Maintenance Tips:
Proper maintenance is essential for the reliable operation of the EGR system. Common issues include clogging of the EGR valve or cooler, sensor malfunctions, or carbon buildup. Regular inspection and cleaning can help prevent these problems. It is also important to use high-quality fuel and engine oil to minimize deposits. If issues arise, consulting a qualified technician and following the manufacturer’s guidelines for troubleshooting and maintenance is advisable.
Pros and Cons of EGR Systems:
The pros and cons of EGR systems may vary depending on the specific engine design, application, and emission regulations. Let’s have a look:
- Advantages of EGR in Terms of Emissions and Efficiency: EGR systems offer significant benefits in reducing emissions, particularly nitrogen oxides (NOx). By recirculating exhaust gases, the combustion temperature is lowered, resulting in reduced NOx formation. EGR also contributes to improved fuel efficiency by reducing pumping losses and minimizing the need for enrichment during high-load conditions.
- Drawbacks and Limitations of EGR Implementation: EGR systems have certain drawbacks and limitations. They can increase particulate matter (PM) emissions due to the presence of recirculated exhaust gases. Additionally, EGR can lead to carbon buildup and fouling of components, potentially affecting engine performance and reliability. Furthermore, EGR systems require careful calibration to balance emission reduction with maintaining engine power and response.
- Future Developments and Alternatives to EGR
- The automotive industry is continuously exploring advancements and alternatives to EGR systems. Some developments include using more advanced EGR cooling technologies, incorporating selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, and implementing exhaust after-treatment technologies. Furthermore, the emergence of electrification and hybridization in vehicles provides alternative paths for reducing emissions without relying solely on EGR systems.
Final thoughts,
Hope, you have got a clear idea about what an exhaust gas recirculation system actually is from the above discussion. EGR systems play a vital role in reducing emissions, improving engine longevity, and increasing fuel efficiency. By recirculating exhaust gases, EGR helps mitigate the formation of harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx), contributing to cleaner air and environmental sustainability.
While EGR offers advantages in terms of emission reduction and fuel efficiency, it also presents challenges such as increased particulate matter (PM) and maintenance requirements. Nonetheless, with ongoing advancements and alternative technologies, you can prevent EGR valve failure, and it will continue to be a crucial component in the pursuit of sustainable engine technologies.
FAQs
Q: What are the symptoms of EGR failure?
A: Symptoms of EGR failure may include rough idle, reduced engine performance, increased emissions, engine stalling, and illuminated check engine light (CEL) indicating EGR system malfunction.
Q: What sensor controls the EGR valve?
A: The EGR valve is typically controlled by the Engine Control Unit (ECU) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM), which receives input from various sensors such as the throttle position sensor and engine coolant temperature sensor.
Q: What is the working principle of the EGR valve?
A: The EGR valve works by opening and closing to regulate the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. It is controlled by the engine control unit (ECU) based on engine conditions to achieve the desired EGR flow rate.
